Wood to Metal
Wood to Metal Glue: Strongest Adhesive in Independent Test
To glue wood to metal, there are different glues and adhesives available. In an independent wood to metal adhesive strength test carried out by Ultimate Handyman, Adiseal was found to be the strongest adhesive by far, finishing over 3 times stronger than the next best product.
We will also look at other methods of attaching wood to metal, look at the positives negatives of each method, how to stick metal to wood together using an adhesive and what is the best adhesive to attach metal to wood.
- What is the best wood to metal glue?
- Why Adiseal is the best to glue metal to wood
- How to glue metal to wood
- Where to buy wood to metal adhesive glue
What is the best wood to metal glue?
In an independent wood to metal adhesive strength test, Adiseal adhesive sealant has been shown to be the strongest adhesive to glue metal to wood together.

Why Adiseal is the best to glue metal to wood
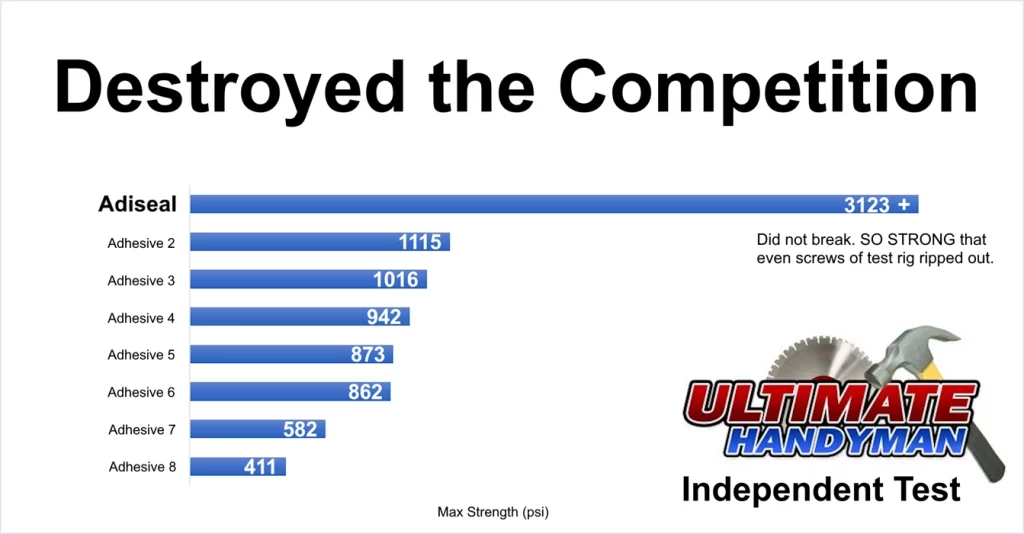
Adiseal construction adhesive sealant is the best product at sticking wood and metal together. In an independent wood to metal adhesive strength test by Ultimate Handyman, Adiseal was easily the strongest adhesive by far. It was over 3 times stronger than the nearest competitor in the wood to metal adhesive bond strength test. In fact, it was so strong that the screws holding the metal sheet down started to rip out forcing the test on Adiseal to be stopped. The table below shows the results of the test.
Strongest Wood to Metal Glue Test Results
- Adiseal : 3123 + psi
- SupaBond : 1115 psi
- Tec 7 : 1016 psi
- HB42 : 942 psi
- Loctite PL Premium : 873 psi
- Gorilla Grab Adhesive : 862 psi
- Bond It PU18 : 582 psi
- Bond It Saves Nails : 411 psi
“That is actually unbelievable!”
Ultimate Handyman
Testimonials
Other benefits of Adiseal
Some of the other reasons why Adiseal is the best product to use when trying to to bond wood to metal:
- Adiseal is the record breaking strongest adhesive & sealant. It proved it’s the best in an independent adhesive strength test by Ultimate Handyman.
- Adiseal stays permanently flexible so it will absorb any vibration and allow any items to expand & contract without the adhesive becoming weak.
- Adiseal is a waterproof sealant and waterproof adhesive so it is also suitable for use outdoors or indoors. It works it dry, wet & even underwater.
- As long as the surface is clean of any dust, grease, paint or any other dirt, priming the material should not be required.
- Adiseal does not soak into wood so sealing of the wood is not required. It can also be used to seal metal.
- It has very high gap fill properties.
- Adiseal has high initial grab meaning temporary supports may not be required while the adhesive cures. Adiseal Hi-Grab has even higher grab than the standard product.
- It is suitable for use of softwood, hardwood & all metals.
- EC1 Pus certified (No VOC)
Problems with epoxy adhesives
Using epoxy adhesives to bond metal to wood presents challenges:
- Inflexibility: Epoxy’s rigidity weakens bonds over time due to temperature and moisture changes, leading to brittleness and breakage. Wood’s moisture absorption and metal’s thermal expansion worsen this issue.
- Complex Mixing: Epoxy’s two-component system needs precise ratio measuring and thorough blending for optimal properties; incorrect mixing leads to subpar results.
- Low Initial Grip: Epoxy’s weaker initial hold demands temporary support during curing, raising time, labor, and cost, in contrast to Adiseal’s superior initial grip.
Problems with mastic adhesives
Mastic adhesives have challenges when used to bond metal to wood:
- Weak Initial Bond: Mastic’s weak grip suits light indoor items but not heavy-duty use.
- Lack of Waterproofing: Not waterproof, unsuitable for wet areas like bathrooms and kitchens.
- Inflexibility: Similar to epoxy, mastic’s rigidity weakens the bond, more so with wood’s moisture-induced expansion or contraction.
- Low Initial Grip: Mastic’s weak initial hold demands temporary support during curing, adding time and labor costs.
Problems with contact adhesives
Contact adhesives serve lightweight sheet bonding, but lack suitability for heavy-duty use and have specific issues:
- Weak Initial Grip: Contact adhesives need temporary support during curing due to low initial hold.
- Limited Gap Fill: Poor gap filling results in weaker bonds between surfaces not closely positioned.
- Porous Wood Sheets: MDF or chipboard absorbs liquid glues, necessitating pre-sealing before adhesive application.
Problems with using glue
Glues work for lightweight bonding on usually smooth surfaces, but not for heavy-duty tasks. For robust heavy-duty bonding, choose Adiseal construction adhesive, as glues have inferior gap fill, initial grip, bond strength, and flexibility compared to Adiseal.
Also, certain wood sheets like MDF or chipboard absorb liquid glues, necessitating pre-sealing before adhesive application for effective bonding.
Does wood glue work on metal
Most wood glues like PVA wood glue will only provide a weak bond on metal. Products like Adiseal adhesive sealant is designed to provide a more durable high-strength bond on both metal and wood.
How to glue metal to wood

How to glue wood to metal
- Remove gaps
Try to make sure there are no big gaps between the surfaces where the adhesive will be applied. If there are any big gaps then either cut or file down the surface of the wood or metal so that they match closely when the wood & metal are put together.
- Preparation of the metal
When attempting to attach wood to metal, preparing both the wood & metal is vital to achieving a good strong long lasting bond.
To prepare the metal surface, make sure the surface is clean of any dust, grease, oil, paint, rust or any other dirt. - Preparation of the wood
To prepare the wood surface, make sure the surface is clean of any dust, grease, oil, paint or any other dirt.
- Apply glue or adhesive
Once both wood & metal surfaces are clean, they are ready for the glue or adhesive. Wood will absorb certain glue’s or adhesives, therefore require sealing prior to applying the glue or adhesive. If Adiseal adhesive & sealant is used then there is no need to seal the wood as Adiseal will not soak into the wood. Cover as much surface area as possible to get the best bond.
- Push wood and metal together
With Adiseal, simply apply the adhesive to either the wood or metal and push the metal and wood together.
- Temporary supports
As Adiseal has high grab, temporary supports should not be required but if the item does start to slide down, then place temporary supports to hold the items in place until the adhesive has cured. Adiseal usually takes 24 hours to 48 hours to fully cure, with curing times increasing in colder temperatures.
Tip: If bonding wood to metal where there is a chance of water, apply the adhesive in thin vertical strips. This allows any water to run down between the strips instead of building up on top of the adhesive. If there is a build up of water between the wood & metal, in cold temperatures it will turn to ice which expands putting additional forces on the adhesive.
Tip: To store Adiseal once opened, leave about 1cm worth of product out of the nozzle and store the tube upright in a cool dry place. Adiseal requires moisture for it to cure. The exposed part out of the nozzle will cure creating a cap. To re-use Adiseal, pull the cured part out or cut the nozzle until the uncured part is reached.
Glue wood to metal with Adiglue
It is also possible to glue wood to metal using our Adiglue. Although Adiglue is less brittle than super glues, it is still not as flexible or strong as Adiseal adhesive sealant.
Stick metal to wood with Adiseal Hi-Grab
The Adiseal Hi-Grab instant grab adhesive will also stick metal to wood. It has a higher initial grab than Adiseal adhesive and sealant. We however recommend the Adiseal adhesive & sealant when attaching metal to wood. The reason for this is because the Hi-Grab product is a very thick product. To push together the 2 items that need sticking together requires a lot bigger force if a thick product like Adiseal Hi-Grab adhesive is between the items. Due to its thick formulation, Adiseal Hi-Grab adhesive also requires a good quality sealant gun (caulking gun) to get the product out of the tube.
Glue or adhesive vs mechanical fixings
It’s possible to attach wood to metal with either glue or mechanical fixings. There are advantages and disadvantages to both methods. One key disadvantage of using mechanical methods like using screws to attach wood to metal is the final finish. A hole will need to be drilled in the wood and the metal. This hole will be permanently visible when the items need to be removed. Even with the screw still in, the screw will still be visible and ruin the look of the wood. An example is in the image below where wooden skirting boards were fitted with screws instead of glue or adhesive.

Sometimes using both glue or adhesive together with mechanical fixings to attach metal to wood can increase the strength of the joint.
Mechanical fixings
It is also possible to attach metal to wood with mechanical fixings. One way would be to drill metal and drill wood then use mechanical fixings. Adiseal Ultimate metal drill bit drills faster and drills more holes than any other metal drill bit.
Where to buy wood to metal adhesive glue
In the UK, to buy wood to metal adhesive or glue for metal to wood, contact us for details of your local stockist. For other countries visit www.guglue.com
Frequently asked questions about glue wood to metal
To attach wood to metal, use the record breaking strongest adhesive, Adiseal. In an independent wood to metal adhesive strength test, Adiseal was over 3 times stronger than the nearest competitor. Make sure both surfaces are thoroughly clean before applying the adhesive.
The best product to use is the record breaking strongest Adiseal. In an independent wood to metal adhesive strength test, Adiseal was over 3 times stronger than the nearest competitor.
Adiseal will attach metal to wood without screws. In a wood to metal adhesive strength test, Adiseal was over 3 times stronger than the nearest competitor. Make sure both surfaces are thoroughly clean before applying the adhesive.
To adhere wood to metal, there are several options available. Adiseal will provide a very strong, long lasting and flexible bond. In an independent test, it has shown to be the strongest adhesive between wood and metal. To adhere wood to metal with Adiseal, first make sure both surfaces are thoroughly clean. Apply the adhesive to 1 surface. Push both items together and hold until the adhesive dries. Temporary supports might be required until the adhesive fully cures.
There are various types of adhesives suitable for wood to metal bonding, including polymer, epoxy, polyurethane, construction adhesive, and cyanoacrylate (super glue). The choice depends on factors such as the specific materials, application requirements, and desired bond strength.
Both surfaces should be clean, dry, and free from dust, grease, or any other contaminants. It may be necessary to roughen the metal surface and remove any rust, while wooden surfaces may need to be sanded or stripped of finishes for better adhesion.
Most types of wood can be successfully bonded to metal using appropriate adhesives. However, some oily or resinous woods may require special surface preparation or priming to ensure a strong bond.
The bond strength depends on factors such as the adhesive type, surface preparation, and the materials being bonded. When properly applied, adhesives can create strong and durable bonds suitable for many applications.
Some adhesives are specifically formulated to provide moisture resistance or outdoor durability. Check the product specifications or consult the manufacturer to ensure the adhesive is suitable for the desired environmental conditions.
Disassembling bonded wood and metal parts can be challenging, especially with strong adhesives. In some cases, heating or applying solvents may help weaken the bond, but it’s advisable to plan the project with the understanding that the bond may be permanent.
